Emerald ash borer discovered in Lincoln, Neb.
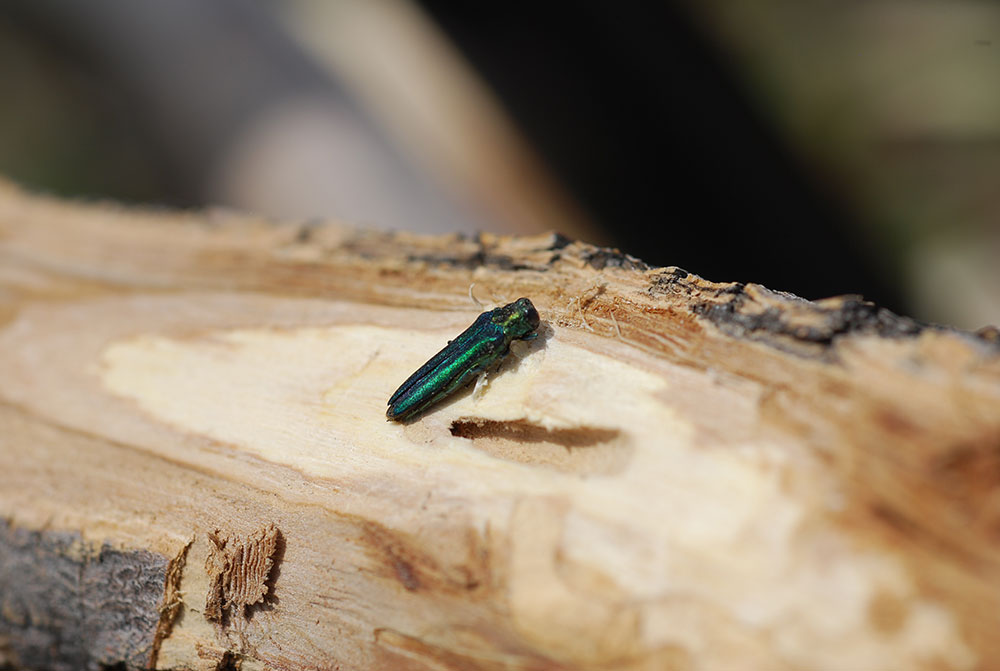
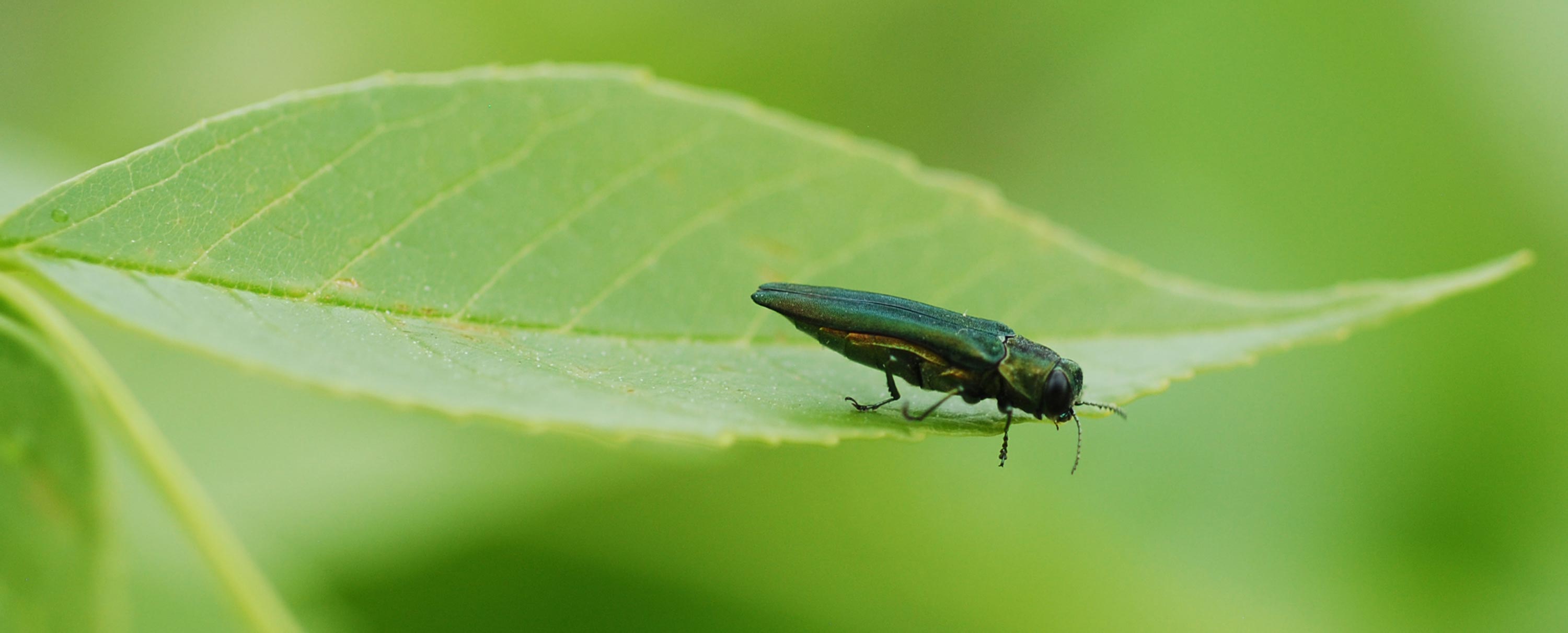
LINCOLN, Neb. — Emerald ash borer (EAB) was first found in Nebraska in June 2016, but it has now been discovered in Lincoln, the state’s second largest city. The news was confirmed by the Nebraska Department of Agriculture (NDA) in partnership with the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) on Aug. 22.
Previously, the NDA had confirmed infestations in Cass and Douglas counties. Douglas County is where Omaha, Nebraska’s largest city, is located. In addition to the discovery in Lincoln, the NDA also reported signs of an infested tree in the smaller town of Fremont, which is approximately 50 miles north of Lincoln.
“While it’s unfortunate we found EAB in Lincoln and signs of an infested tree in Fremont, it is not unexpected considering we have confirmed EAB infestations in Douglas and Cass counties,” NDA Director Steve Wellman said.